In an era marked by heightened awareness of health, sustainability, and authenticity, the concept of natural food has gained considerable traction. But what does it truly mean for a food to be labeled ‘natural’? Delving deeper than mere marketing buzzwords, this article elucidates the multifaceted nature of natural food, exploring its origins, characteristics, benefits, and the pivotal role it plays in shaping contemporary culinary landscapes and consumer choices.
1. Defining Natural Food:
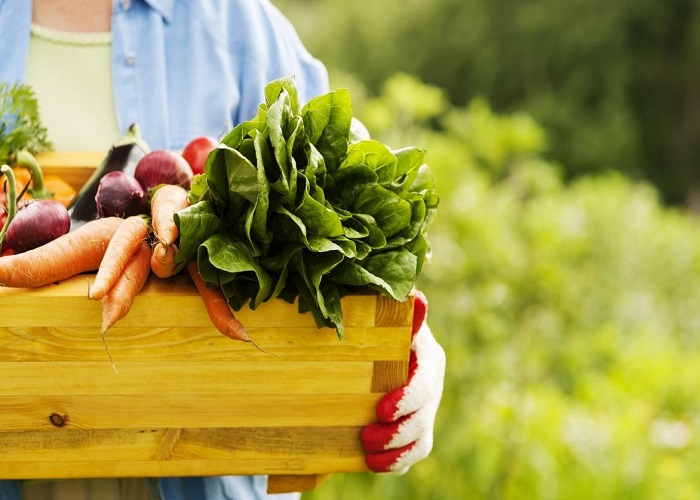
Natural food refers to food items that are minimally processed and free from synthetic additives, preservatives, and genetic modifications. These foods are often recognized for their authenticity, nutritional richness, and alignment with traditional and sustainable farming practices. It encompasses a wide range of categories, including fruits, vegetables, whole grains, nuts, seeds, legumes, and sustainably sourced proteins. They prioritize whole, unadulterated ingredients, preserving their innate flavors, textures, and nutritional profiles. Embracing foods promotes healthful eating habits, supports environmental sustainability, and fosters transparency within the food supply chain, emphasizing the importance of ethical sourcing, responsible production, and conscious consumption.
2. Natural Food Qualities
It is celebrated for its authenticity, purity, and inherent nutritional richness. Embodying the essence of unaltered nature, these foods resonate with individuals seeking healthful, sustainable, and transparent dietary choices. Here are some defining qualities that characterize natural foods:
- Minimal Processing: Natural foods are minimally processed, preserving their original textures, flavors, and nutritional profiles. Unlike heavily processed foods that undergo extensive refining, bleaching, or chemical alterations, natural foods retain their innate qualities, ensuring optimal nutrient retention and authentic taste.
- Whole Ingredients: At the heart of natural foods lie whole, unadulterated ingredients. From vibrant fruits and vegetables to whole grains, legumes, and sustainably sourced proteins, these foods prioritize whole ingredients in their purest form, free from synthetic additives, preservatives, or genetic modifications.
- Transparency and Traceability: Natural foods champion transparency within the food supply chain. By emphasizing ethically sourced, locally grown, and sustainably harvested ingredients, they foster connections between producers and consumers. This transparency cultivates trust, accountability, and a deeper appreciation for the origins and journey of food from farm to plate.
- Nutritional Excellence: Rich in essential vitamins, minerals, antioxidants, and phytonutrients, natural foods offer unparalleled nutritional value. They support optimal health, vitality, and well-being, contributing to disease prevention, energy metabolism, and overall physiological balance.
- Environmental Harmony: Strain natural foods align with principles of environmental sustainability. By supporting organic farming practices, biodiversity conservation, and regenerative agriculture, natural foods mitigate environmental degradation, promote soil health, and foster ecological balance.
3. Benefits of Natural Food:
- Nutritional Superiority: Natural foods are inherently rich in essential vitamins, minerals, antioxidants, and phytonutrients. They provide optimal nourishment, supporting overall health, immune function, and disease prevention.
- Enhanced Digestive Health: Free from synthetic additives, preservatives, and artificial ingredients, natural foods are more digestible and less likely to cause digestive discomfort or inflammation, promoting gut health and optimal digestion.
- Reduced Chemical Exposure: Natural foods are produced without the use of synthetic pesticides, herbicides, and genetically modified organisms (GMOs). By minimizing chemical exposure, they support cellular health, detoxification processes, and reduce the risk of chronic diseases associated with environmental toxins.
- Support for Sustainable Agriculture: Choosing natural foods supports sustainable and regenerative agricultural practices. By prioritizing organic farming, biodiversity conservation, and soil health, natural foods contribute to environmental sustainability, climate resilience, and ecological balance.
- Ethical Considerations: Embracing natural foods aligns with ethical considerations, promoting animal welfare, fair labor practices, and responsible production methods. By supporting ethical food systems, consumers play a pivotal role in fostering transparency, accountability, and social responsibility within the food industry.
- Holistic Well-being: Natural foods nourish not only the body but also the mind and spirit. They foster a deeper connection to nature, promote mindfulness in eating habits, and encourage a more conscious and intentional approach to nourishment and self-care.
- Flavor and Culinary Diversity: Natural foods boast authentic flavor profiles and diverse culinary possibilities. By embracing seasonal, locally sourced, and sustainably harvested ingredients, individuals can explore a rich tapestry of flavors, textures, and cultural culinary traditions, enhancing the gastronomic experience.

4. Challenges and Considerations: Navigating the Natural Landscape
Misleading Marketing:
The pervasive use of ‘natural’ labels in marketing necessitates vigilance. Not all products labeled as natural align with consumers’ expectations of purity and authenticity. Scrutinizing ingredient lists, understanding labeling regulations, and seeking third-party certifications can aid in making informed choices.
Accessibility and Affordability:
Despite the burgeoning demand for natural foods, accessibility and affordability remain barriers for many consumers. Addressing these challenges requires collaborative efforts from stakeholders across the food supply chain to foster equitable access to quality natural products.
5. Cultivating a Natural Food Lifestyle:
- Educate and Empower: Begin by educating yourself about the principles and benefits of natural foods. Stay informed about current research, farming practices, and food labeling standards. Empower yourself with knowledge to make informed and conscious choices that align with your values and health goals.
- Prioritize Whole Foods: Emphasize whole, unprocessed, and nutrient-dense foods in your diet. Incorporate a colorful array of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, legumes, nuts, seeds, and sustainably sourced proteins to ensure a diverse and balanced nutrient intake.
- Choose Organic and Local: Whenever possible, opt for organic and locally sourced foods. Organic farming practices prioritize soil health, biodiversity, and natural ecosystems while supporting local farmers fosters community connections, reduces environmental impact, and ensures freshness and seasonality.
- Mindful Meal Planning: Adopt mindful meal planning and preparation techniques. Plan weekly menus, incorporate seasonal ingredients, and allocate time for cooking and enjoying meals. Engage all senses while eating, savoring flavors, textures, and aromas, and fostering a deeper appreciation for the nourishing qualities of natural foods.
- Support Sustainable Practices: Support brands, producers, and retailers committed to sustainable and ethical practices. Look for certifications such as USDA Organic, Non-GMO Project Verified, Fair Trade, and others that align with your values and sustainability criteria.
- Reduce Waste: Embrace a zero-waste approach to minimize food waste and environmental impact. Practice mindful shopping, utilize leftovers creatively, compost organic waste, and prioritize reusable and eco-friendly packaging options.
- Engage in Community: Engage with local farmers’ markets, community-supported agriculture (CSA) programs, and organic food cooperatives. Build connections with producers, artisans, and fellow enthusiasts, fostering a sense of community, shared values, and collaborative learning.
- Lifelong Learning: Cultivate a mindset of lifelong learning and exploration. Experiment with new recipes, culinary techniques, and global cuisines enriched with natural foods. Stay curious, open-minded, and receptive to evolving insights and perspectives within the natural food movement.
- Practice Mindful Eating: Adopt mindful eating practices to cultivate a deeper connection with food and enhance the eating experience. Practice gratitude, savor each bite, chew slowly, and listen to your body’s hunger and satiety cues, fostering a harmonious relationship with food and promoting optimal digestion and well-being.
Conclusion:
Natural food, with its emphasis on purity, authenticity, and holistic well-being, transcends mere dietary choices to encompass broader principles of sustainability, environmental stewardship, and conscious living. As consumers increasingly prioritize transparency, quality, and ethical considerations in their food selections, the significance of natural foods resonates profoundly. By cultivating awareness, making informed choices, and advocating for sustainable practices, individuals can embrace the essence of natural food, fostering a healthier, more harmonious relationship with food and the environment.